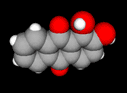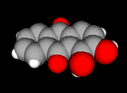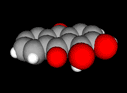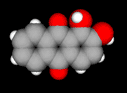
About the chemical structure:
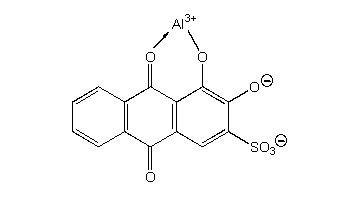
| Chemical name: | Alizarin (1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone), Purpurin (1,2,4-trihydroxyanthraquinone) |
| Formula: |
C14H8O4, C14H8O5 |
| 3D model: |
grey = carbon, red = oxygen, white = hydrogen |
| Refractive index: | Madder lake: 1.66; alizarin: 1.70 |
Color:
| Color Index (C.I.) | NR 9 |
How can you identify Madder lake ?
Imaging:
UVF: no
IRFC: orange

Beccafumi, 1486-1551, Tuscany, Italy
The red gown of the Virgin sohws up in orange, being painted with madder lake.
OM: The base on which both varieties are substrated is indistinguishable under the microscope. Nor can the natural and artificial be identified even at high magnification.
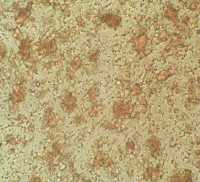
Microscopic appearance at x500 mag
Analytics:
It's identified by means of FTIR.
FTIR spectra: IRUG
Usage and handling:
| Permanence: | Toxicity: |
|---|---|
Lightfast: excellent Degradation processes: One of the most stable organic pigments/dye stuffs. |
non toxic. The essential coloring matter of the madder root is considered to be non-toxic. MSDS: Kremer |
Literature:
Artists’ Pigments. A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics, Vol 3: E.W. Fitzhugh (Ed.) Oxford University Press 1997, p. 109 - 142.
Stössel, I., Rote Farblacke in der Malerei - Herstellung und Verwendung im deutschsprachigen Raum zwischen ca. 1400-1850, Publikationsreihe des Instituts für Malerei Stuttgart, 1985
Koch, H. M. und Pfeifer, P., Naturfarbstoffe im Unterricht. Antrachinonfarbstoffe der Krappwurzel. Praxis der Naturw.-Chemie, 10, 1999, s. 25-29